H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES
H C Verma Physics Solutions for Exercise - H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 13: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 1] solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section (figure). The area of the cross-section at and are and , respectively. If of water enters per second through , find the speed of the water at , the speed of the water at and
the pressure difference .

Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section (figure). The area of the cross-section at and are and , respectively. of water enters per second through . If the tube is kept vertical with upward but the other conditions remain the same, the separation between the cross-sections at and is . Find the speed of the water at , the speed of the water at and the pressure difference . Take .

Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section(figure). The area of the cross-section at and are and , respectively. If the tube is kept vertical with upward, the separation between the cross-sections at and is . Water enters through at the rate of . Find the speed of water at , the speed of water at and the pressure difference . Take .

Water flows through a tube, as shown in the figure. The areas of the cross-section at and are and , respectively. The height difference between and is . If the speed of the water at is , find the speed at and the difference in pressures at and
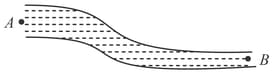
Water flows through a horizontal tube, as shown in the figure. If the difference of heights of the water column in the vertical tubes is and the areas of the cross-section at and are and , respectively, find the rate of flow of water across any section.
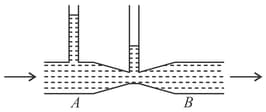
Water flows through the tube, as shown in the figure. The areas of the cross-section of the wide and the narrow portions of the tube are and , respectively. The rate of flow of water through the tube is . Find the difference in the mercury levels in the -tube.
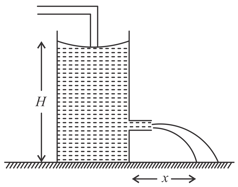
Water leaks out from an open tank through a hole in the area at the bottom. Suppose water is filled up to a height of and the area of cross-section of the tank is . The pressure at the open surface and at the hole is equal to the atmospheric pressure. Neglect the small velocity of the water near the open surface in the tank.
Find the initial speed of water coming out of the hole.
Find the speed of water coming out when half of the water has leaked out.
Find the volume of water leaked out during a time interval after the height remained is . Thus, find a decrease in height in terms of and .
From the result of part , find the time required for half of the water to leak out.
The water level is maintained in a cylindrical vessel up to a fixed height . The vessel is kept on a horizontal plane. At what height above the bottom should a hole be made in the vessel, so that the water stream coming out of the hole strikes the horizontal plane at the greatest distance from the vessel?